Carbon Tracking Apps for Businesses: Driving Sustainability
In today's world, environmental concerns are crucial in addressing climate change, placing corporate sustainability at the center of strategic decisions. Companies globally are not just monitoring but actively reducing their carbon footprints. Carbon tracking apps are emerging as vital tools in this shift, providing innovative ways for businesses to assess, control, and lessen their environmental impact. This blog post delves into the expanding world of carbon tracking applications, their role in corporate sustainability efforts, and the steps to develop a strong carbon-tracking solution.
Table of content
Table of Contents
We’re on board to help with your product. Don’t hesitate to get in touch.
Contact Us Let’sTalk
In today’s world, environmental concerns are crucial in addressing climate change, placing corporate sustainability at the center of strategic decisions. Companies globally are not just monitoring but actively reducing their carbon footprints. Carbon tracking apps are emerging as vital tools in this shift, providing innovative ways for businesses to assess, control, and lessen their environmental impact. This blog post delves into the expanding world of carbon tracking applications, their role in corporate sustainability efforts, and the steps to develop a strong carbon-tracking solution.
Unveiling the Fabric of Corporate Sustainability
The pursuit of a sustainable future is now a central directive for stakeholders throughout the corporate world. At the heart of this movement is the complex task of carbon management, which involves measuring and managing the carbon emissions produced by businesses. Amid global agreements and increasing public awareness, the focus on tracking and reducing these emissions has moved beyond environmentalist discourse to become a key element of corporate strategy.
The Hierarchies of Corporate Carbon Emissions
Corporate carbon footprints are categorized into three ‘scopes’ in the context of their direct and indirect environmental impact.
- Scope 1 relates to direct emissions from sources that are owned or controlled by the company, including onsite fuel combustion and process emissions.
- Scope 2 comprises greenhouse gas emissions stemming from the consumption of purchased electricity, heat, or steam.
- Scope 3, the broadest category, encompasses all other indirect emissions that occur in a company’s value chain.
Emission Sources and Industry Variance
While industrial emissions contribute significantly to global carbon levels, the sources of these emissions vary extensively.
- The utility sector generates a substantial portion through electricity and heat production.
- Manufacturing and construction yield emissions due to energy usage and chemical processes.
- Transportation and logistics add to carbon footprints through the burning of fossil fuels, such as internal combustion engines.
Environmental Impact and Corporate Responsibility
The implications of unabated carbon emissions are manifold, from the exacerbation of climate change-related disasters to the environmental degradation of air, water, and soil. Corporations, as major contributors, bear a consequential responsibility to realign their operations with ecologically sustainable practices.
Navigating the App-Infused Emission Tracking Landscape
Carbon tracking applications have emerged as indispensable tools in monitoring and managing carbon footprints, offering real-time data analytics and visualization essential for corporate sustainability.
Apps as Environmental Guardians
The integration of carbon tracking apps enables proactive emissions management.
- Real-time Monitoring and Incident Response: Instantaneous visibility into emissions allows for swift remedial action in the event of unforeseen spikes or critical system failures that cause emissions.
- Precise Data for Compliance: Detailed and accurate data provide the evidence required for compliance with environmental regulations and standards, shielding companies from penalties and reputational damage.
Strategic Decision Making and Efficiency Gains
Carbon tracking technology empowers businesses to make informed decisions that enhance both environmental and operational efficiencies.
- Improved Operational Performances: By identifying areas of excessive emissions, companies can streamline processes and workflows to optimize energy use and waste management, ultimately reducing costs.
- Forecasting and Risk Management: The ability to forecast emission trends supports strategic risk management, allowing businesses to anticipate changes and align operations with sustainability goals.
Crafting the Ideal Carbon Tracking Interface
A successful carbon tracking app excels in user experience and offers an array of features that cater to the contemporary corporate environment.
User-Centric Design and Functionality
User satisfaction is paramount in app design, with clear functionality and intuitive navigation.
- Dynamic Dashboards: Visualizations on emission trends and impacts are crucial for understanding and decision support, requiring a user-friendly dashboard.
- Seamless Integrations: Compatibility with existing corporate systems ensures that emissions data is integrated into broader operations and strategies without friction.
Advanced Analytical Capabilities
In-depth analysis tools provide the insights necessary to drive sustainability initiatives.
- Predictive Modeling: Advanced algorithms and machine learning can predict future emissions based on historical data, supporting long-term strategic planning.
- Custom Reporting: The app should facilitate the generation of reports tailored to the needs of various stakeholders, from sustainability teams to executive management.
Scalability and Customizability
An effective carbon tracking app must be both scalable, to accommodate growing emissions tracking needs, and customizable, to suit the diverse requirements of different industries and companies.
Composing the App Development Symphony
Developing a carbon tracking app combines strategic planning, technology, and user needs. This development process starts with defining the app’s purpose and audience. It can serve internal stakeholders in a specific industry or target a broader commercial market. Each development stage must align with user goals and technological expectations. The final product should not only be functional but also promote sustainable practices effectively.
Setting the Objectives
The initial step in crafting a carbon tracking application involves a detailed analysis of its goals. For developers, this means determining whether the app is intended for internal purposes within a specific sector, such as manufacturing or logistics, or if it is aimed at a wider public market. This decision will guide the app’s design and functionality, ensuring it meets the specific needs of its users. For example, an app designed for corporate use might focus on integrating with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems, while a consumer-facing app could prioritize ease of use and immediate feedback on carbon footprint reduction.
Selecting the Right Technology Stack
Selecting the right technology stack is crucial. It involves choosing backend, frontend, API, and database technologies that support the app’s scale and performance needs. This decision impacts development speed and scalability. For instance, cloud-based solutions can provide flexibility, while a microservices architecture might support a complex app ecosystem. Technologies like React or Angular for frontend and Node.js or Python for backend shape the app’s efficiency and user experience.
Data Privacy and Security
Data privacy is critical in carbon tracking due to the sensitive nature of the data. Strong security measures like data encryption and secure API endpoints are essential. Practices should include using HTTPS, encrypting stored data, and conducting regular security audits. These measures protect user data and build trust, which is vital for adoption.
User Experience Design
The success of a carbon tracking app often hinges on its user experience (UX) design. This involves creating an interface that is not only visually appealing but also intuitive and responsive to the user’s needs. UX designers must understand the typical workflow of their target audience, whether they are individuals looking to reduce their personal carbon footprint or businesses aiming to comply with regulatory requirements. The design process should focus on minimizing user effort while maximizing engagement and functionality, perhaps through personalized dashboards or interactive elements that make tracking and reducing emissions both simple and rewarding.
Piloting and Iterating
Employing a phased rollout for the app allows developers to integrate real-time feedback from early users, facilitating continuous improvements and fine-tuning of the app. This iterative process can help identify and fix bugs, enhance features, and refine the user interface for better accessibility. Starting with a pilot group of users, developers can gather valuable insights that drive iterative updates, ensuring the app not only meets but exceeds user expectations. This approach not only improves the quality of the app but also aids in building a loyal user base that feels invested in the product’s evolution.
Addressing the Hindrances in Carbon App Development
The development of carbon tracking applications presents unique challenges that must be skillfully navigated to ensure the app’s success. These challenges range from technical issues, such as integrating diverse data sources, to user engagement and regulatory compliance. Each obstacle requires a dedicated strategy to overcome, whether through advanced coding techniques, user education, or adaptive legal frameworks, making the process complex yet rewarding for developers committed to environmental sustainability.
Data Collection and Accuracy
The effectiveness of a carbon tracking app heavily relies on the precision and timeliness of the data it processes. To ensure reliability, the app must seamlessly integrate with various data sources, such as sensors and public databases, and employ robust validation techniques to verify the accuracy of the data. This might include implementing algorithms that detect anomalies in data patterns or cross-referencing inputs from multiple sources to minimize errors. These measures are crucial to provide users with dependable insights into their carbon emissions, enabling informed decision-making.
Technical Hurdles
As technology evolves, so must carbon tracking apps. Developers face the ongoing challenge of adapting to new technologies and maintaining the app’s relevance in an ever-changing digital landscape. This requires a commitment to continuous learning and innovation, leveraging the latest developments in software engineering and environmental science. By embracing modern programming frameworks and staying ahead of technological trends, developers can ensure their applications remain effective and competitive.
Change Management
Introducing a new technology, especially one that requires a change in user behavior, often encounters resistance. Effective change management strategies are essential to facilitate the adoption of the carbon tracking app across organizations. This may involve comprehensive training sessions, regular stakeholder engagement, and clear communication about the benefits and functionalities
The Beacon of Emerging Carbon Management Technologies
The carbon tracking field is on the verge of transformative change, with artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT) poised to revolutionize environmental monitoring. These advanced technologies enhance the precision and effectiveness of carbon management systems, enabling dynamic and adaptive strategies. Consequently, they allow businesses and governments to better monitor emissions and implement timely sustainability initiatives, steering us toward a more sustainable future.
AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are reshaping carbon tracking by providing predictive analytics. These tools help businesses anticipate future emission levels using historical data and trend analysis. Consequently, companies can simulate scenarios and strategize to minimize their carbon footprint ahead of time. This proactive approach is crucial not only for regulatory compliance but also for reducing environmental impact effectively, thus supporting corporate sustainability.
Blockchain for Transparency
Blockchain technology introduces unmatched transparency in carbon management by creating an immutable emissions data ledger. This ensures that records are permanent and unalterable once entered. Moreover, the inherent transparency fosters trust among all stakeholders, including regulators, businesses, and the public, facilitating more reliable and transparent carbon management practices. Thus, blockchain is becoming an indispensable tool in the quest for environmental accountability and sustainability.
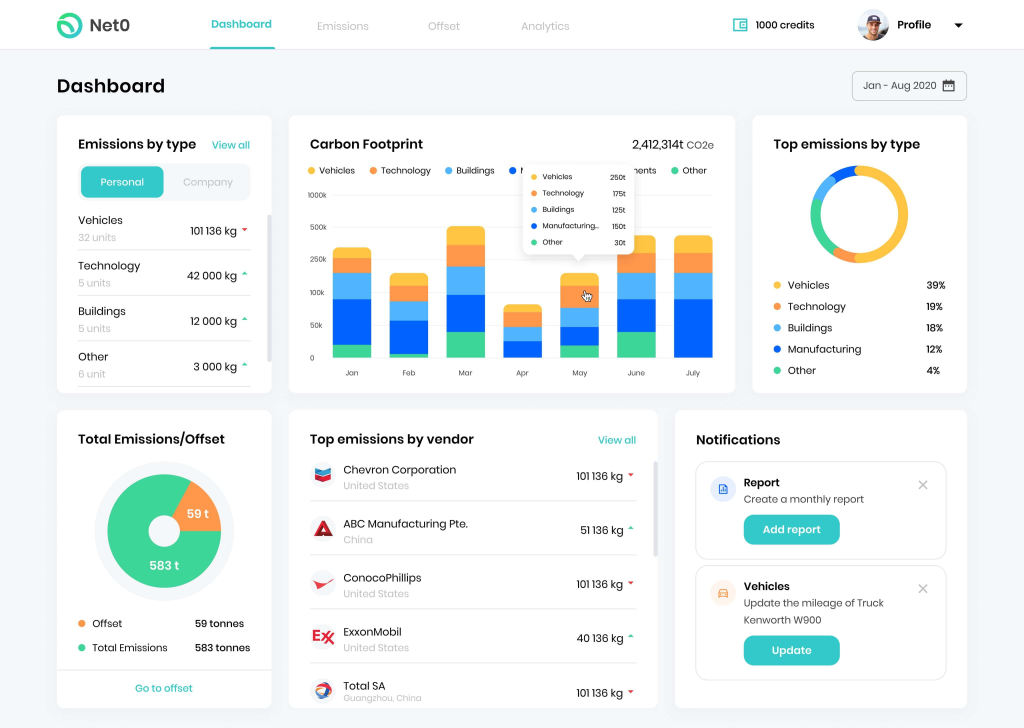
IoT for Real-time Sensing
The Internet of Things (IoT) expands the capabilities of emissions tracking by enabling real-time monitoring through a network of interconnected devices. This development allows for continuous surveillance of emissions from a wide range of sources. As a result, businesses can receive instant data on their emissions, making it easier to adjust practices promptly and maintain compliance with environmental standards. Moreover, real-time data collection through IoT devices supports more nuanced and immediate responses to potential environmental impacts.
Sprinting Towards a Green Horizon
As we advance towards a future where corporate sustainability is essential, carbon tracking apps are becoming crucial tools. These applications not only assess our current environmental footprint but also guide businesses towards more sustainable practices. Additionally, for companies aiming to reduce their environmental impact while remaining profitable, these apps are proving to be invaluable allies. Their role in enhancing sustainability measures is indispensable as we strive for a greener and more responsible corporate landscape.
How to Catalyze Change within Your Organization
The call to action for corporate leaders is clear. It is time to evaluate existing carbon management strategies and consider the adoption or development of carbon tracking apps. Initiatives can begin with small but significant steps, such as integrating third-party carbon tracking tools, before venturing into proprietary applications.
Envisioning a Sustainable Future
The vision for a sustainable future is not merely an environmental stipulation but a corporate imperative. The development and implementation of carbon tracking apps are earmarks of this vision, encapsulating the ethos of responsible business practices. By advocating for and investing in these technologies, enterprises can carve out a legacy that harmonizes with humanity’s stewardship of the planet.


